Shielded Window Material Types
Glass
Advantages – scratch resistance, resistance to solvents/chemicals, non-flammable
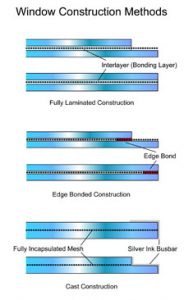
Usual construction method – fully laminated, sometimes edge bonded
Types – low coefficient of expansion borosilicate glass, toughened
Surface finishes – etched anti-reflective, magnesium fluoride or multilayer antireflective
Polycarbonate
Advantages – impact resistance/toughness, low density, low or non-flammable
Usual construction method – fully laminated, edge bonded
Types – UL94-V0 flammability or low smoke emission grades, range of tints
Surface finishes – scratch/mar, solvent and chemical resistant hard surface coating, this coating can be applied as
Acrylic
Advantages – clarity, low density
Usual construction method – fully laminated, cast or edge bonded
Types – wide range of tints
Surface finishes – scratch/mar resistant hard surface coating, antireflective coating
Cast polyester (CR39)
Advantages – clarity, low density, scratch resistance, high-temperature stability, resistance to solvents/chemicals
Usual construction method – cast or cast/laminated assembly
Types – wide range of tints
Surface finishes – ‘cast in’ anti-reflective finish
Special purpose polarising or contrast enhancement filters may be incorporated within windows. In particular cast windows lend themselves to this as the filter may be cast in at the time of manufacture.